Virtual reality (VR) is a term used for computer-generated 3D environments that allow the user to enter and interact with alternate realities. The users are able to “immerse” themselves to varying degrees in the computers artificial world which may either be a simulation of some form of reality or the simulation of complex data.
The term “Virtual Reality” (VR) was initially coined by Jaron Lanier. Founder of VPL Research (1989).
The technology : Virtual Reality
There are some people to whom VR is a specific collection of technologies; that is. headset,glove and walker.VR is defined as a highly interactive, computer-based multimedia environment in which the user becomes the participant in a computer-generated world. It is the simulation of a real or imagined environment that can be experienced visually in the three dimensions of width, heigth and depth and that may additionally provide an interactive experience visully in full real-time motion with sound and possibly with tactile and other forms of feedback.VR is a way for humans to visualize, manipulate and interact with computer and extremely complex data.
The components necessary for building and experiencing VR are divided into two main components-the hardware components and the software components.
Hardware components
The hardware components are divided into five sub-components
-
Computer workstation
A computer workstation is a high-end microcomputer designed for technical or scientific
applications.
-
Sensory displays
Sensory displays are used to display the simulated virtual worlds to the user. The most
common sensory displays are the computer visual display unit, the head-mounted display
(HMD) for 3D visual and headphones for 3D audio.
Head mounted display
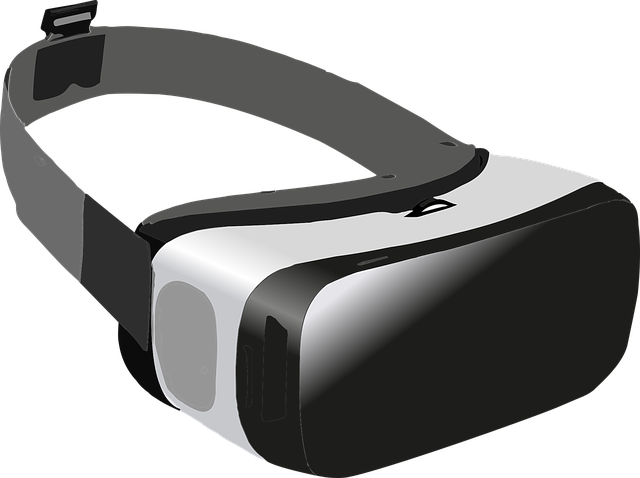

Head mounted displays place a screen in front of each of the viewer’s eyes at all times.
Binocular Omni-Orientation Monitor (BOOM)
The BOOM is mounted on a jointed mechanical arm with tracking sensors located at the
joints.
Software components
The software components are divided into four sub-components.
-
3D modeling software
3D modeling software is used in constructing the geometry of the objects in a virtual world and specifies the visual properties of these objects.
-
2D graphics software
2D graphics software is used to manipulate texture to be applied to the objects which enhance their visual details.
-
Digital sound editing software
Digital sound editing software is used to mix and edit sounds that objects make within the virtual environment.
-
VR simulation software
Simulation software brings the components together. It is used to program how these objects behave and set the rules that the virtual world follows.
Classification of Virtual Reality systems
VR is classified into three major types:
- Non-immersive VR systems – As the name suggests, are the least implementation of VR techniques.
- Semi-immersive VR systems – A semi immersive VR system comprise of a relatively high performance graphics computing system which can be coupled with either a large screen monitor.
- Immersive (fully immersive) VR systems – An Immersive VR system is the most direct experience of virtual environments.
How Virtual Reality works
The idea behind VR is to deliver a sense of being there by giving at least the eye what it would have received if it were there and, more important to have the image change instantly as the point of view is changed (Smith & Lee, 2004). The perception of spatial reality is driven by various visual cues, like relative size, brightness and angular movement. One of the strongest is perspective, which is particularly powerful in its binocular form in that the right and left eyes see different images. Fusing these images into one 3D perceptions the basis of stereovision.
The perception of depth provided by each eye seeing a slightly different image, eye parallax,is most effective for objects very near you. Objects farther away essentially cast the same image on each eye. The typical dress code for VR is a helmet with goggle-like displays, on for each eye. Each display delivers a slightly different perspective image of what you would see if you were there. As you move your head, the image rapidly updates so that you feel you are making these changes by moving your head (versus the computer actually
following your movement, which it is. You feel you are the cause not the effect.
Modern VR Experiences
The current generation of VR systems was brought about by advances in display, sensing, and computing technology from the smartphone industry.
DORA Telepresence Robot
Remote presence robots, as the name implies, act as your stand-in at a distant location, letting you move around and see and hear through a robotic surrogate.

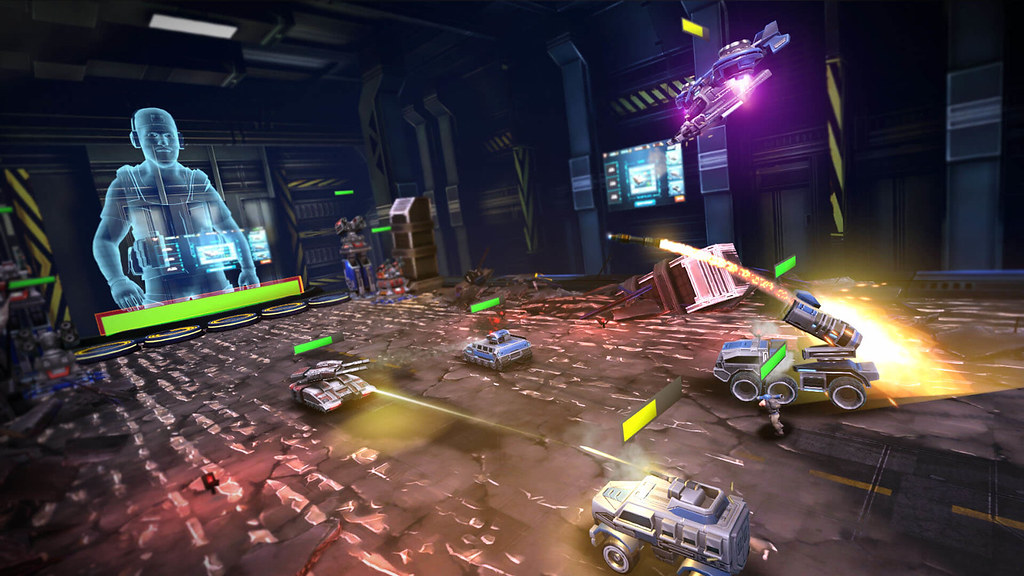
Video games
People have dreamed of entering their video game worlds for
decades. By 1982, this concept was already popularized by the Disney movie Tron.
Most gamers currently want to explore large, realistic worlds through an avatar. Below image shows a game that contrasts all the others in that it was designed to specifically exploit the power of VR.

Immersive cinema

VR Cinema, developed in 2013 by Joo-Hyung Ahn for the Oculus Rift.
Viewers could choose their seats in the theater and watch any movie they like.
Telepresence

An important component for achieving telepresence is to capture a
panoramic view: (a) A car with cameras and depth sensors on top, used by Google to make Street View. (b) The Insta360 Pro captures and streams omnidirectional videos.
Health care

A heart visualization system based on images of a real human heart.
This was developed by the Jump Trading Simulation and Education Center and the University of Illinois.
Augmented reality
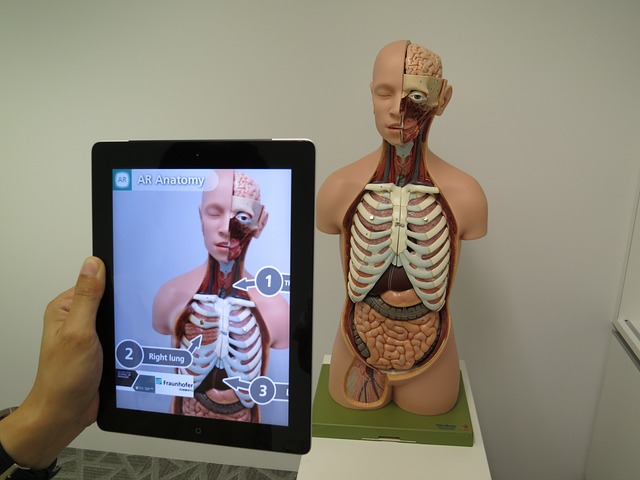
In many applications, it is advantageous for users to see the live, real world with some additional graphics superimposed to enhance its appearance.

The Microsoft Hololens, 2016, uses advanced see-through display
technology to superimpose graphical images onto the ordinary physical world, as perceived by looking through the glasses.